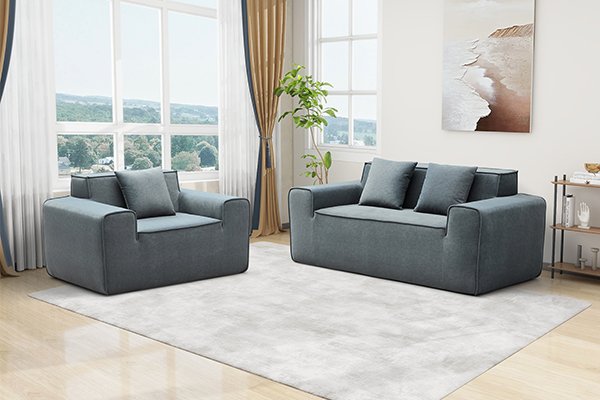

Compressed sofas are an innovative solution to reduce costs and improve logistics in the furniture industry. But how exactly are they made, and what ensures their quality?
Compressed sofas are made through a specialized process that involves selecting durable materials, assembling the sofa, preparing it for compression, and using advanced machinery to reduce its size.
This carefully engineered process ensures that the sofa retains its functionality and comfort even after being compressed. Let’s break it down step by step.
Step 1: Material Selection
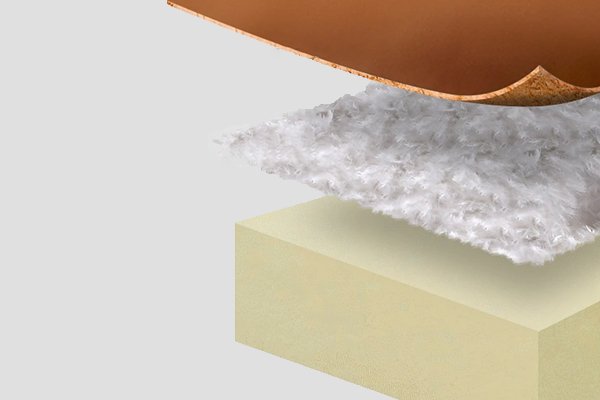

The foundation of a high-quality compressed sofa lies in the materials used. These materials must be durable enough to withstand compression and regain their shape upon unpacking.
Manufacturers use flexible and resilient materials, such as high-density foam, pocket springs, and modular frames, to ensure the sofa retains its integrity after compression.
Common Materials Used
- Foam: High-density foam for cushioning and comfort.
- Springs: Pocket springs for flexibility and durability.
- Frames: Lightweight yet sturdy materials like hardwood or metal.
Material Comparison
| Material | Purpose | Compression Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| High-Density Foam | Provides comfort | Excellent |
| Pocket Springs | Ensures flexibility | Very Good |
| Hardwood Frames | Structural support | Good |
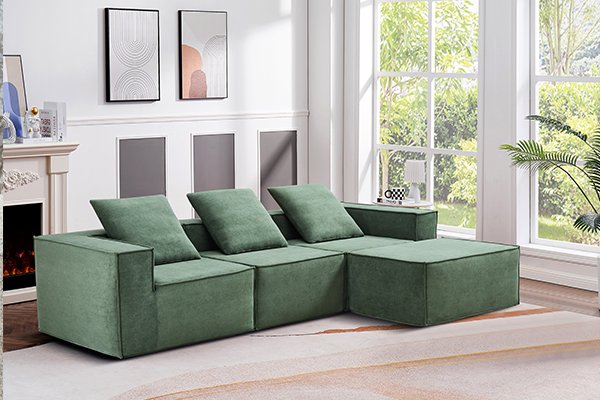
Step 2: Assembly and Design

Once the materials are prepared, the sofa is assembled. Design plays a critical role in ensuring the sofa is suitable for compression.
Modular designs are often used to simplify the compression process and make the sofa easy to reassemble after unpacking.
Key Features of Compressed Sofa Design
- Detachable Components: Arms, legs, or cushions may be removable for easier compression.
- Compact Frames: Designed to flatten without breaking.
- Flexible Upholstery: Stretches during compression and returns to its original state.
Step 3: Preparation for Compression

Before compression, the sofa undergoes preparation to protect it during the process. Proper preparation is essential to prevent damage.
The sofa is cleaned, wrapped in protective materials, and sealed in a vacuum bag to ensure it remains intact during compression and transport.
Steps in Preparation
- Cleaning: Ensures no dust or debris is trapped inside.
- Wrapping: Protective layers like bubble wrap or foam are applied to cushion the sofa.
- Sealing: A vacuum bag removes air and creates a compact package.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Insufficient Wrapping: Can lead to scratches or dents.
- Low-Quality Seals: May allow air to re-enter the package.
- Over-Compression: Can damage materials if not carefully controlled.
Step 4: Compression Process

The compression process uses advanced machinery to reduce the sofa’s volume while maintaining its quality. This step is the most critical in manufacturing a compressed sofa.
Specialized hydraulic compressors and vacuum sealing machines are used to flatten the sofa evenly and ensure airtight packaging.
Machines Used in Compression
| Machine Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Hydraulic Compressors | Apply even pressure to compress materials |
| Vacuum Sealers | Remove air to create compact packaging |
| Wrapping Machines | Secure protective layers around the sofa |
Key Considerations During Compression
- Pressure Control: Prevents over-compression that could damage materials.
- Uniform Compression: Ensures all parts of the sofa are evenly flattened.
- Quality Testing: Each unit is inspected to ensure it meets standards.
Step 5: Packaging and Shipping
After compression, the sofa is boxed for shipping. Sturdy packaging ensures it arrives at its destination in perfect condition.
Boxes are designed to be compact yet durable, protecting the sofa during transport while keeping the overall size and weight minimal.
Packaging Features
- Reinforced Cardboard: Protects the compressed sofa.
- Clear Instructions: Simplifies unpacking and assembly for customers.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Aligns with sustainability goals.
Conclusion
Compressed sofas are made through a meticulous process involving material selection, modular design, careful preparation, and advanced compression technology. This ensures they are space-saving, cost-efficient, and durable, meeting the demands of modern consumers.